Authors: Martakov I.S., Torlopov M.A., Mikhaylov V.I., Krivoshapkina E.F., Silant’ev V.E. , Krivoshapkin P.V.
Abstract
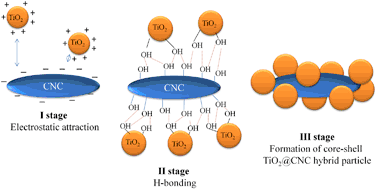
In this work we prepared hybrid particles based on cellulose nanocrystals and titanium dioxide nanoparticles and studied their aggregate stability for a wide range of the components ratios. Electrosurface properties of cellulose nanocrystals and TiO2 greatly influence on morphology and properties of the hybrid particles. Sufficient amount of TiO2 nanoparticles in the hybrid dispersions make it possible to completely cover cellulose nanocrystals surface and form a core-shell structure. Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek theory calculations confirmed experimental data and possibility of TiO2 monolayer covering of cellulose nanocrystals surface. Summarizing the findings, we conclude about the mechanism of interaction between cellulose nanocrystals and titanium dioxide—at the first stage particles are attracted to one another due to long-range electrostatic forces; at the second stage hydrogen bonds are formed. It is found that control of the surface potential allows to obtain stable colloidal hybrid dispersions (having negative-charged or positive-charged particles), or hybrid systems with a neutral surface charge.
DOI: doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4447-3
Read Full: